Margin Advice

As retailers worldwide look to transition their business models to focus heavily on ecommerce and dropship, there is a core question posed: what are our margin requirements?
The process in which retailers use to arrive at their requirements is highly individual. Some retailers leverage their incredible buying power to squeeze margin out of their suppliers down to the percentage point. Other retailers are far more flexible on requirements and will sacrifice points as a tradeoff for priority service, co-marketing expenses, and more.
Whereas an expert in any industry could quickly spout their industry-specific wholesale margins, dropship margins are much more of a gray area. This article outlines factors a retailer should consider when setting their margin requirements for their sellers.
General Advice
Firstly, it is critical to identify the product categories that you intend to be (or already are) carrying on your marketplace. This helps determine the degree to which your product category margins will be standard or if sellers expect to negotiate their margins with you.
A core difference between dropship and wholesale is the degree to which margins are standard across different categories. Whereas a wholesale markup of 50% off retail is standard across many industries and product types, dropship markups are lower (typically between 20%-35%) and fluctuate much more broadly across categories.
To streamline your own operations, it is advisable to standardize your margins per-category as much as possible. Pricing negotiations may be necessary but often can be avoided if the initial margin proposed is consistent with margins the seller would find elsewhere.
Also consider factors such as shipping and returns. Sellers who offer to handle all returns logistics often retain a couple of percentage points to offset their increased cost of doing business. However, this drastically reduces a retailer’s logistical burden. We strongly advise retailers to have all costs accounted for in the unit-level price and for sellers to cover the cost of shipping.
The last factor to consider is that fees for the consumer purchase are paid by the retailer as part of their merchant services account, because retailers own the financial relationship with the consumer. Fees associated with the retailer’s payment to the supplier (such as Stripe payment gateway fees) are paid by the supplier and should be incorporated into their wholesale margin.
Sample Legal Terms
Below are sample legal terms that can be used as a template for your own contracts:
[Brand Name] agrees to pay the monthly fees negotiated by [Retailer Name] to keep [Brand Name]’s products on [Retailer Name]. Failure to pay the monthly fee will result in immediate delisting of [Brand Name]’s products on [Retailer Name].
Implementation
Pricing negotiations are one of the most easily streamlined parts of seller onboarding.
The easiest method is to ask for flat margins across categories and have sellers embed their cost of shipping into the wholesale price. This allows for flat-rate percentage markups to be applied and an ease of pricing future products.
Percentage Pricing
To establish percentage-based pricing, the seller could first create a price list applying a 25% discount off retail (the retail margin) and apply it to their entire product catalog.
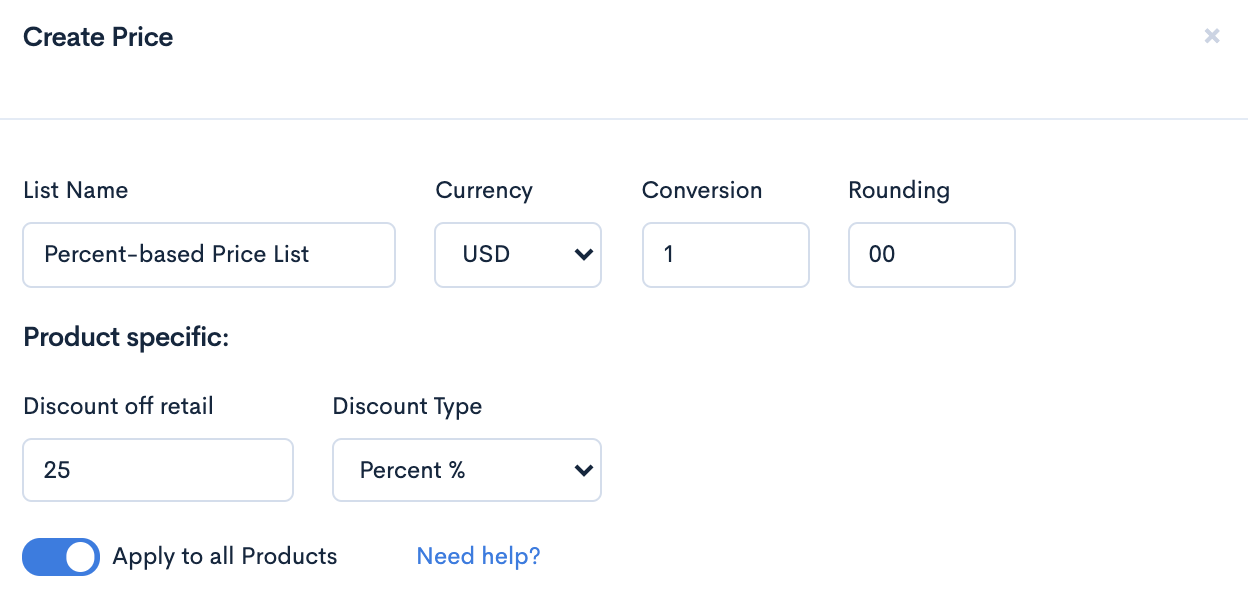
On a per-product basis, this would then appear as such:
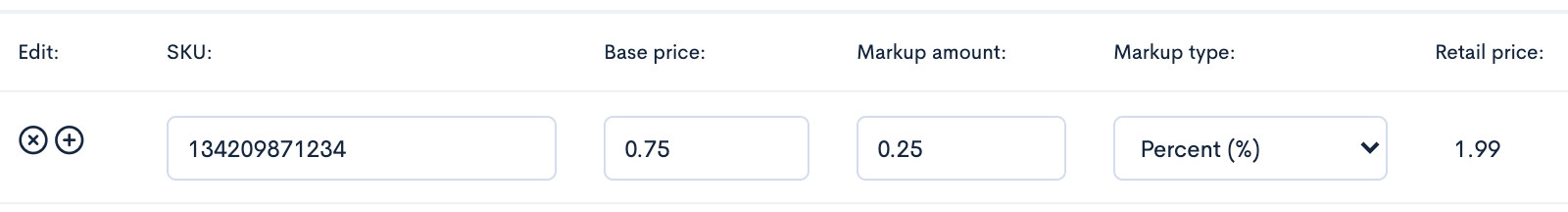
Here we see that the base price is 75% of the total retail price and the markup amount is 25%. Carrying the math across, the seller would earn a $1.50 wholesale margin and the buyer would earn a $0.50 retail margin.
Fixed-rate Pricing
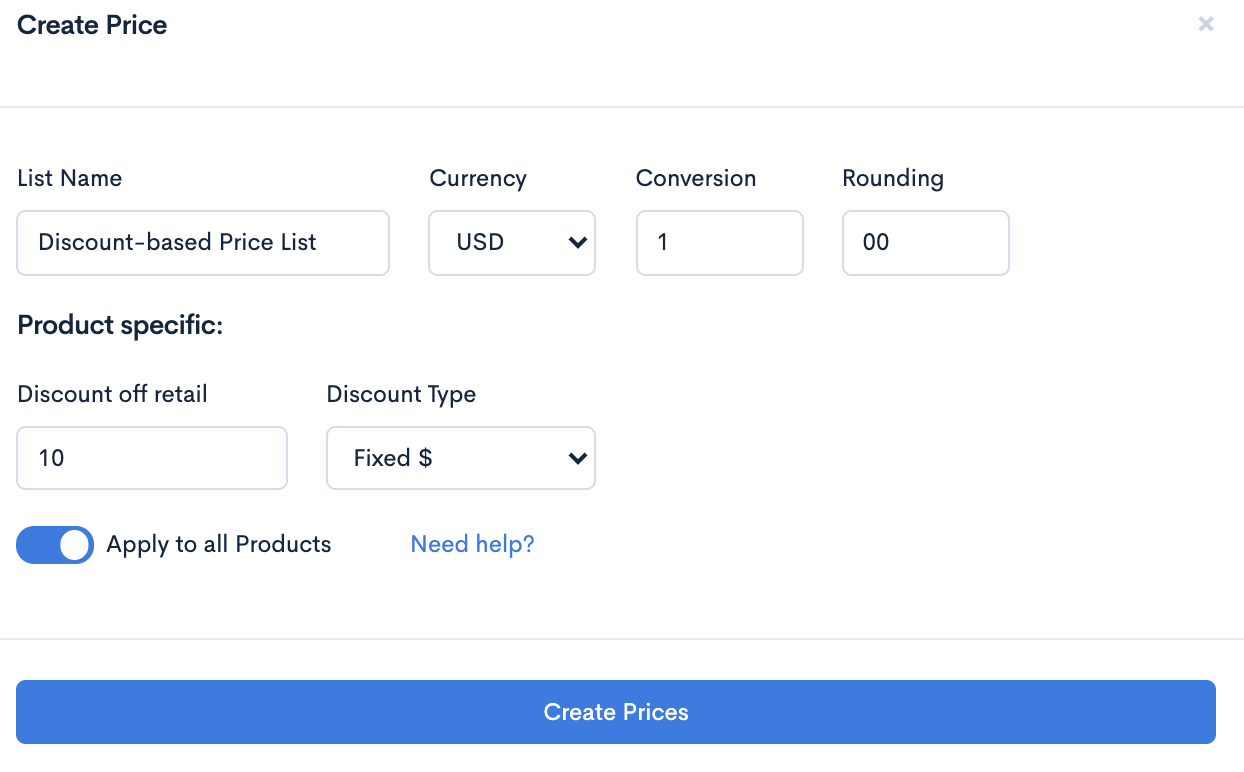
To establish fixed-rate pricing, the seller could first create a price list applying a $10 discount off retail (the retail margin) and apply it to their entire product catalogue.
On a per-product basis, this would then appear as such:
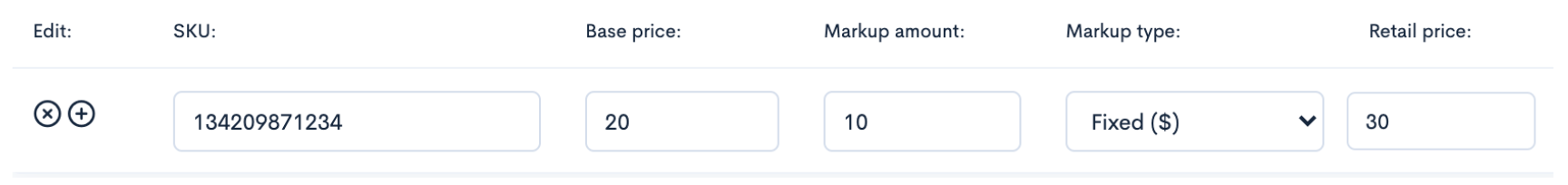
Here we see that the base price is $20 (66% of the total retail price and the markup amount is $10 (33%). Carrying the math across, the seller would earn a $20 wholesale margin and the buyer would earn a $10 retail margin for a total retail price of $30.
It is generally recommended to apply a percentage-based discount across a seller’s product catalogue for ease of use and also to allow for new products to be priced automatically.
Further details on setting up price lists can be found at the How to Setup Pricing support guide.
